1776 to 1900 by binta, Manuel, Ryan, and sean
|
1798
The United States Federal Government has created a law to help traders who travel in ships. People who travel in ships carry diseases with them. Some of the diseases are scurvy and yellow fever. The law created hospitals to help people who travel in ships to trade ("Public Health History Timeline"). |
|
|
1850
Lemuel Shattuck created a document that was extremely important on public health in Boston, Massachusetts.The document talks about what people in Massachusetts should do to fix their public health system. Shattuck gave some ideas about creating a state board of health (“Public Health History Timeline”). Find out more about epidemics, public health, and Shattuck's role. |
|
1895
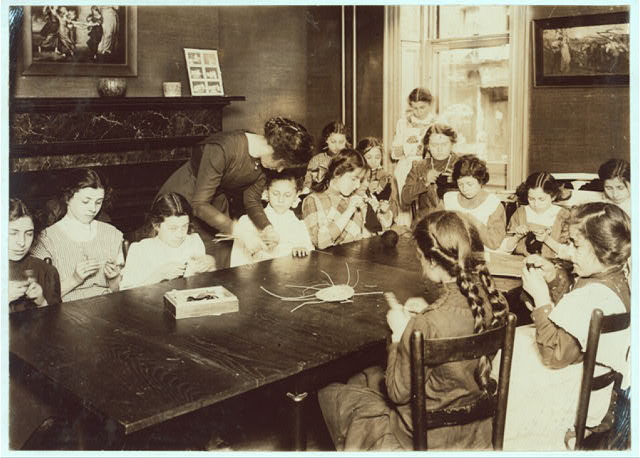
Lillian Wald was a strong woman who helped the needy and immigrants. In 1895, Lillian Wald, created a place where people in need could get help. This place was called Henry Street Settlement. Lillian Wald became known for nursing (“Public Health History Timeline”). Find out more about Lillian Wald. |
1900-1930 by Joey, Kyle, Nick, and Lauralei
|
1900
AMA, the American Medical Association, became a powerful national force. Europeans begin to find more value in insuring against costly illnesses than Americans. Physicians aren’t expected to give free care to all patients in their hospitals. The leading industry to create valuable employee medical programs is the railroad industry. Surgery is now a more common practice. Such as removing tumors, infected tonsils, appendectomies, and gynecological operations. In 1901, AMA returns as the national organization of state and local associations. The members of AMA increased by about 62,000. Starting from about 8,000 physicians during 1900 to 70,000 in 1910. This period in time is known as the beginning of "organized medicine" ("AMA History Timeline"). |
|
|
1910
Hospitals in America have become modern scientific institutions. Now valuing the use of antiseptics and cleanliness in their facilities. Also they began using medications to relieve pain. AALL, American Association for Labor Legislation, organizes first national conference on the subject of “social insurance". Some support seems to be increasing for progressive reformers that argue for health insurance. Conflict rises between physicians and other interest groups. That causes the beginning of the US into the war in 1917 undermines reform effort (PBS). |
|
1920
Health facilities that are located in rural areas have been classified as clearly inadequate compared to health facilities in urban areas. Penicillin is discovered, but its use in the medical field won’t be found till twenty more years. General Motors seals a deal with Metropolitan Life to cover over 180,000 workers with medical insurance. The general mood of political satisfaction has yet to change, so there is no strong effort to change health insurance (PBS). |
1930-1950 by Kendra, Kyleah, Isaiah, and Anonymous
|
1934
The AMA strongly opposes national health insurance because it interferes with doctor patient relationship ("Health Care Timeline"). |
|
1944
Economic Bill of Rights is created which gives people the right to adequate medical care. Businesses begin to offer health care ("Health Care Timeline"). |
|
1945
Proposed restructuring of health care which includes mandatory coverage, more hospitals twice as many doctors/nurses. The public was not in favor of “socialized medicine” and the plan goes nowhere ("Health Care Timeline"). |
|
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
|
1946
The Hill-Burton Act pays for the construction of rural hospitals, “separate but equal" facilities, close gaps in medical care, prohibits discrimination based on race religion or national origin, and requires hospitals to provide “reasonable amount” of charitable care ("Health Care Timeline"). |
1950-1970 by Kylie, Damien, Hung, and Matt
|
1950s
Hospital care prices doubled. The United States creates a system where there is private insurance for people who can afford it and welfare for people who are poor and can’t afford private insurance. Legislatures propose many different approaches to hospital insurance, but none happen. Medications are newly invented to care for different diseases and sicknesses. New vaccines are around to prevent childhood diseases. The first organ transplant is accomplished (“Healthcare Crisis”). |
|
|
|
1960s
Since hospital care doubled in the 1950’s people that have no jobs, especially the elderly, are having a difficult time affording insurance. There are over 700 insurance companies selling insurance in the United States. Health profession education is expanded because of a concern of “doctor shortage” and the need for more “health manpower." Medicare and Medicaid are signed into law by President Lyndon Johnson. The number of full-time specialist doctors rise from 55% to 69% (“Healthcare Crisis”). |
|
1970s
Health maintenance organizations (HMOs) are the new name of prepaid group health care plans by President Richard Nixon. The plans have laws that provide federal endorsement, certification and assistance. Out of nowhere, Medicare consumptions grew fast in the economy due to the growth of hospital visit costs, new changes in medical care, and cautiously moderate approaches to cures made healthcare costs increase. The national health insurance plan is denied. Numbers increase strikingly for women beginning the medical occupation. During the year 1970, 9% of medical students are females and at the end of ten years the amount increases to 25%. The World Health Organization declares smallpox destroyed (“Healthcare Crisis”). |
|
1970-1980 by Brenden, Kayla, Zach, and anonymous
|
|
1971
The National Cancer Act was signed into law: they passed the bill so that it could strengthen the cancer care institute. It helped get a few different branches made. It created the NCAB which is National Cancer Advisory Board. It also made the three-member panel, PCP, that holds periodic public hearings and they submit the hearings for an annual progress report (“Office of Government and Congressional Relations”). Find out more about the National Cancer Act of 1971. |
|
1975
The Child Support Enforcement program was established. The legislation added a public law, 93-647, where they made it so that there was child support. They amended authorities to enforce the state to find nonresident parents and establish them as parents so they can collect child support (“Child Support Enforcement Program”). Find out more about the child support law. |
|
1980
Federal funding was provided to states for foster care and adoption assistance. This required states to make adoption assistance payments to parents who adopt a child who is AFDC-eligible and is a child with special needs. It would grant them money for doing the adoption. Prevents the removal of foster kids and works to get the ones who have been removed back into homes as soon as possible (“Child Welfare Information Gateway Survey Administration – Issue”). |
1980-1990 by Jennifer, Ray, Justin, and anonymous
|
1981
In 1981, a widespread occurrence of an infectious disease known as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) spread all over the world. In 1981, more than 23 million people died because of AIDS. Currently more than million people are still suffering from HIV ("Public Health History Timeline"). |
|
|
1988
The Institute of Medicine issued a plan for a new health care system ("Public Health History Timeline"). |
|
1990
The Ryan White Comprehensive Aids Resources Emergency know as CARE protected everyone who had HIV/AIDS from people discriminating against them ("Public Health History Timeline"). |
1990 by Jordyn, Ramon, Meagan, Duncan
|
1991
When a veterinary surgeon and an orthopedic surgeon came together they created RoboDoc, the first robotic device to perform surgical procedures. The $500,000 technology could cut through human bone 40 times more accurately than a surgeon (Beazley). |
|
1991
The University of Pittsburgh Medical Center achieved a huge milestone when a team at the University transplanted a baboon liver into a 35-year-old patient suffering from Hepatitis B. A baboon was selected because baboons are immune to the disease (Beazley). |
|
1992
At 14%, the Health care spending in the Unites States topped the economic output up from 9.6 percent in 1981. Employers and employees raised $258.5 billion for health care services (Beazley). |
|
1992
In January, The Food and Drug Administration put a ban on the production of silicone breast implants, because of reported defects and numerous health and safety risks. In April, the agency ordered that the implants be removed from the market (Beazley). |
|
1995
To investigate fraud and abuse in Medicare and Medicade, Government agencies started Operation Restore Trust. $187.5 million in recoveries, audits, settlements, various fines, and civil monetary penalties had been lifted, representing a $23 return for every dollar spent. (Beazley). |
|
1998
HCFA offered a reward of 10% of any savings in a constant fight against fraud and abuse. A reward of $1,000 to any Medicare beneficiary who identifies fraud practices (Beazley). |